A television transmitter is an electronic device which radiates radio waves that carry a video signal representing moving images, along with a synchronised audio channel. The television signal is then received by television receivers (televisions or TV sets) belonging to a public audience, which display the image on a screen. TV transmitters must be licensed by governments and are restricted to a certain frequency channel and power level. They are also classified according to the working mode of video and audio modulation, namely, analogue or digital.
The original television technology, analogue, was replaced in a transition which started in 2006 in many countries with digital broadcasting, or DTV. DTV uses number codes to represent images and sound, which can be transmitted using much less of the available radio spectrum than the old analogue signals. The picture quality of DTV is significantly higher than analogue TV and can be displayed in a widescreen format.
TV broadcasters (also known as TV networks or television channels) make their own television programmes. They can also import foreign TV shows or rerun old ones.
The video and audio signals from a programme are sent to the television station’s transmitter where they are converted into electromagnetic waves. The video signal amplitude modulates the RF carrier, whereas the audio signal frequency modulates another RF carrier. These two carriers are combined together and fed into a transmitter antenna where they are transmitted to the broadcasting network.
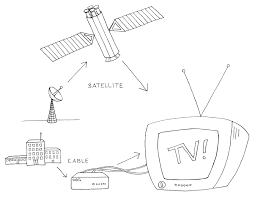
TV signals travel through the air as electromagnetic waves, and can be picked up by any receiver with an antenna. They can be boosted and amplified to reach remote locations, and are often received by satellite dishes which convert the electromagnetic signals into useful signals which can be received by TV sets. For help with TV aerial repair Bristol, go to aerial-installations-bristol.co.uk

A receiver (TV set) turns the received radio waves into electrical signals which it processes to create a TV picture. This can be a flat-screen display or a CRT (Cathode Ray Tube) monitor. The TV set also has speakers that turn the electrical signals into audio.
There are several ways for TV signals to get to a viewer’s home or office. Local TV stations use antennas to send, or broadcast, the signals over the air as radio waves. Cable TV companies transmit the signals through underground cables. And satellite TV transmissions are carried by satellite dishes that pick up the signals from geosynchronous (geolocated) satellites.



